
Today, I want to address what I believe represents the next evolutionary leap: agentic AI applications in healthcare. Unlike passive AI tools that simply process information, agentic systems actively participate in the clinical workflow—observing, reasoning, and taking appropriate actions to support care delivery.
The Current Landscape: Beyond Ambient Scribes
Many clinicians have experience with today’s ambient clinical documentation tools that passively transcribe patient-provider conversations. While these systems reduce administrative burden, their limitations became frustratingly apparent during my time observing clinical practices.
Extending these tools into agents however risks losing the “fuzzy” connectors that exist between physicians and nurses, medical assistants, and administrators.These fuzzy connectors are crucial when asking for clarification or correction. For example, I may poke my head out of my office and say to our staff:
Sina Bari MD: Can you have Ms. Smith follow up with Dr. Jones for cardiac clearance?
Nurse: Do you mean Ms. Jones with Dr. Smith, the cardiologist?
Sina Bari MD: Yes, thank you! That’s what I meant.
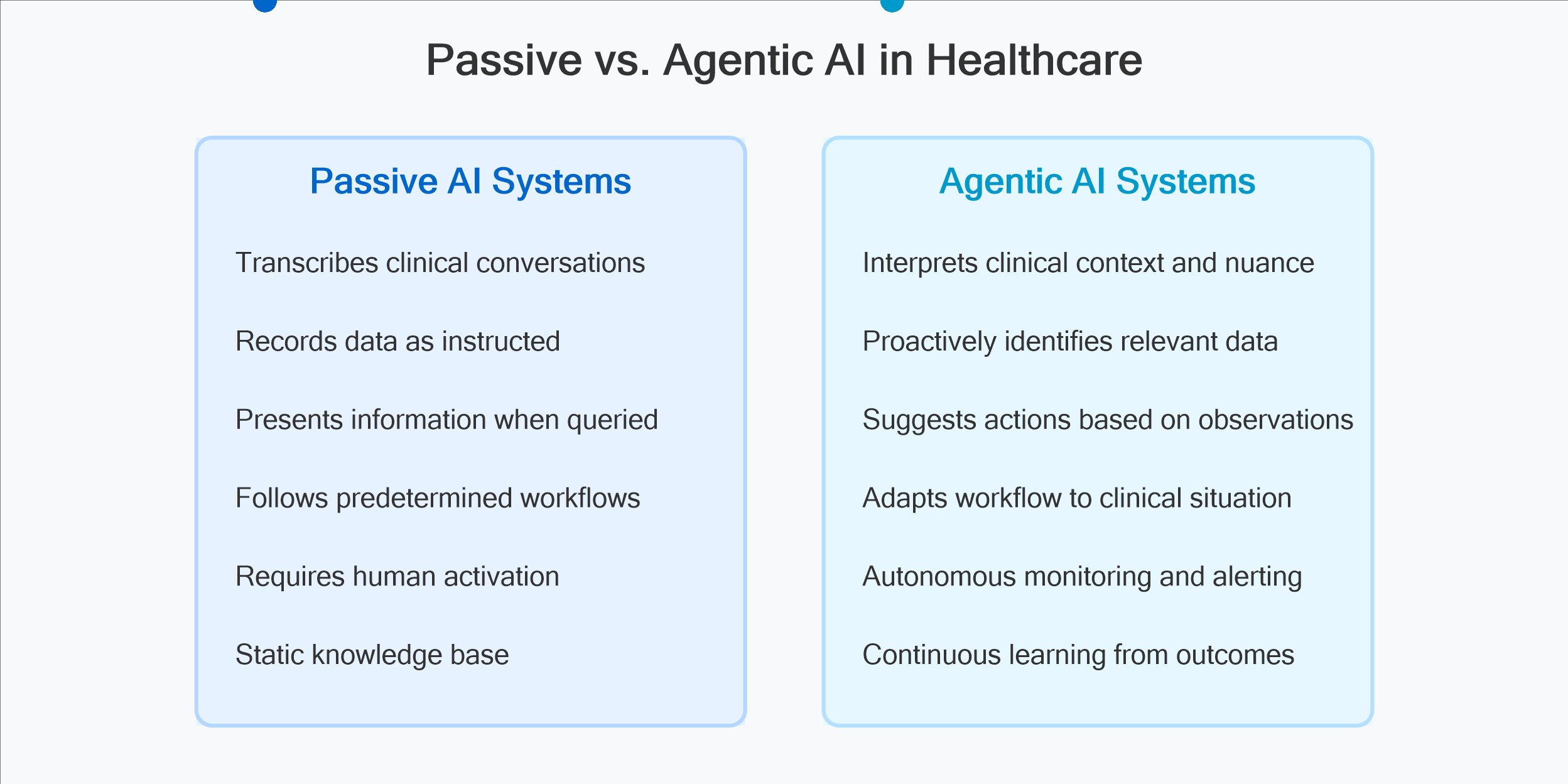
Envisioning Agentic Clinical Systems
True agentic AI functions differently. Rather than simply recording information, these systems actively participate in the clinical workflow, identify decision points requiring intervention, autonomously execute appropriate support actions, and learn continuously from outcomes and feedback.
At iMerit, our medical AI division has been laying the groundwork for these capabilities by developing high-quality training datasets that capture the complexity of clinical decision-making. The work is painstaking but essential—models can only learn the importance of that subtle and fuzzy pathways if we’ve properly structured thousands of similar instances in our training data.
A Timeline for Healthcare Agentic AI
Based on my experience directing medical AI initiatives and clinical observations, here’s how I see agentic AI evolving in healthcare:
ai-healthcare-timeline.svg
2025-2026: Enhanced Ambient Intelligence AI systems that not only transcribe but interpret clinical conversations. Automated linkage of discussion points to relevant medical records. Proactive suggestion of appropriate order sets based on verbal clinical assessment. Intelligent prioritization of information in the EHR interface.
2026-2027: Order Dataset Co-pilots Tentative orders generated from the summaries generated by the ambient scribe. Expanding into the operative, procedural, and nursing administrative spaces.
2027-2028: Clinical Workflow Orchestrators Systems that coordinate care across multiple providers and settings. Autonomous scheduling optimization based on clinical urgency and resource availability. Predictive intervention for deteriorating patients before human detection. Personalized treatment planning incorporating multi-modal patient data.
2031 and Beyond: Collaborative Care Partners AI systems that maintain longitudinal therapeutic relationships with patients. Autonomous monitoring with discretionary clinical intervention. Seamless integration of physical robots and virtual agents in care delivery. True clinical reasoning capabilities approaching physician-level judgment.
The Human-AI Partnership in Practice
Despite my enthusiasm for these technologies, I remain firmly convinced that medicine’s human element cannot be automated away. The art of clinical practice isn’t merely technical precision but understanding each patient’s unique goals and psychological needs.
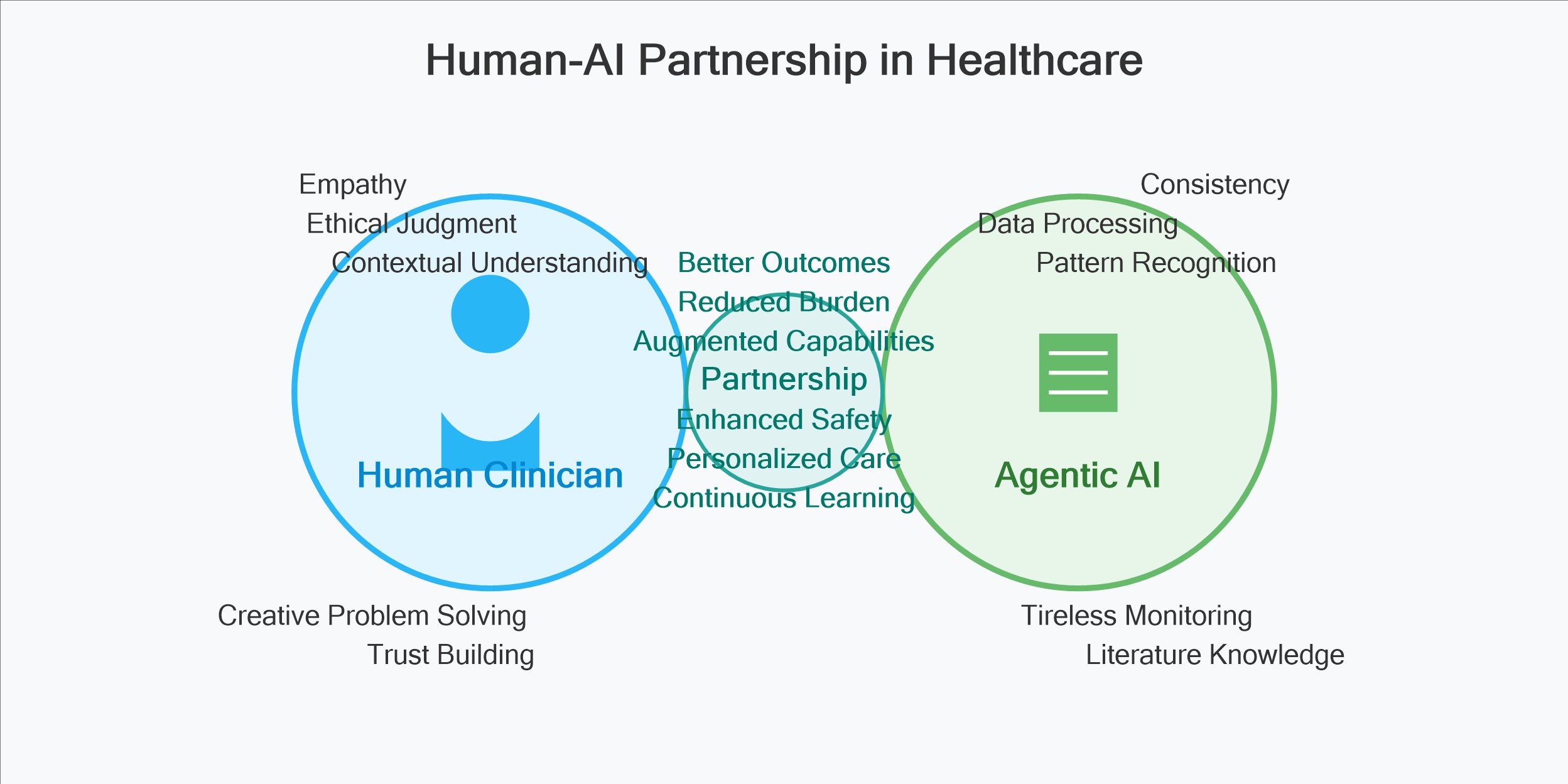
I envision agentic AI as amplifying rather than replacing clinical judgment. During my work developing training modules for medical professionals, I observed how technology could enhance human capabilities rather than diminish their importance. The most successful implementations occurred when clinicians viewed the technology as a collaborative tool rather than a replacement for expertise.
Ethical Considerations and Implementation Challenges
The road to effective agentic healthcare AI contains significant obstacles:
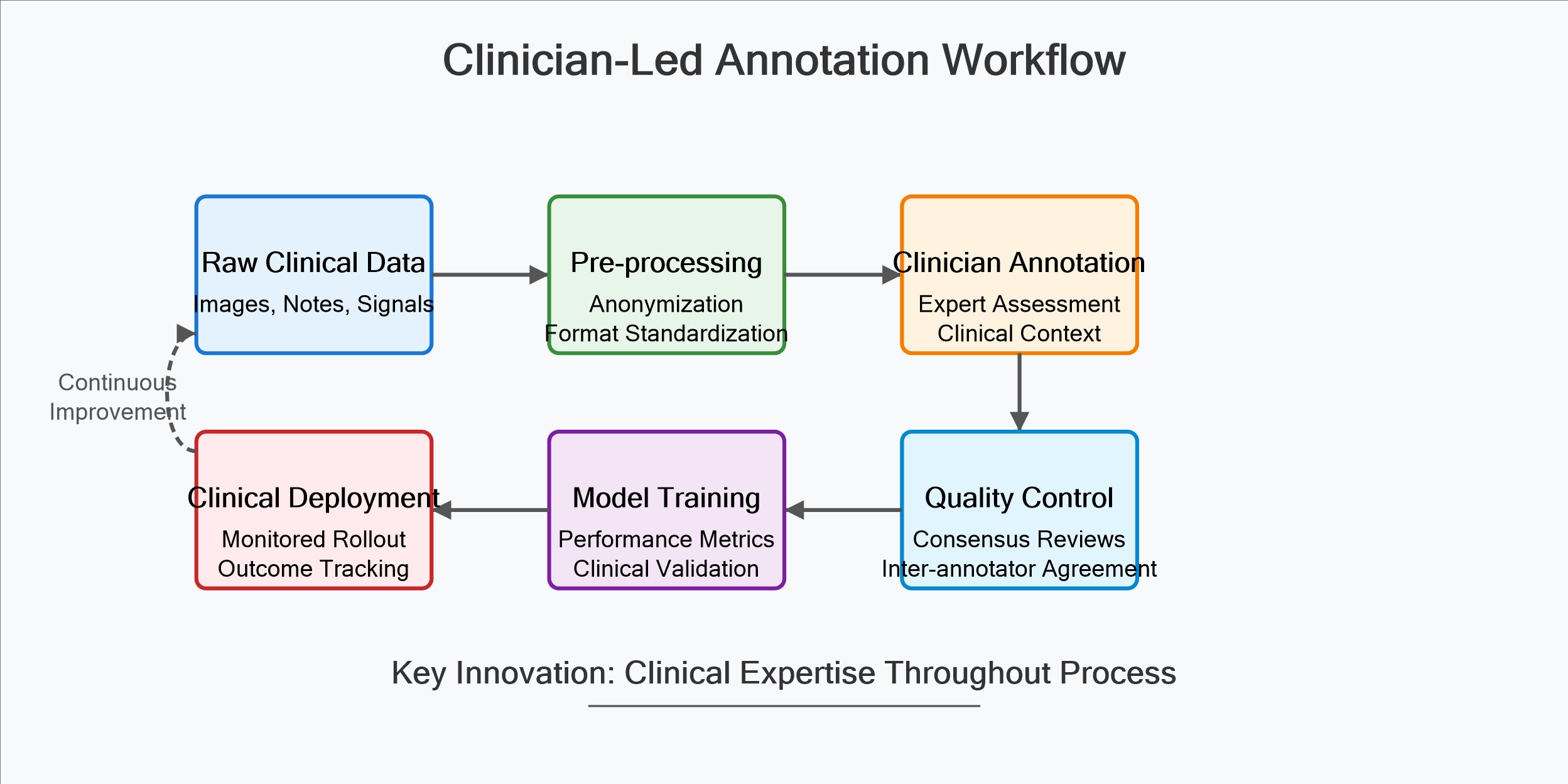
The implementation challenges include clinical validation requiring rigorous evidence of safety and efficacy, workflow integration designing systems that enhance rather than disrupt care delivery, establishing clear liability frameworks for AI-influenced decisions, maintaining patient confidentiality while enabling system learning, and ensuring these tools don’t exacerbate healthcare disparities.
At iMerit, our team addresses these challenges by using dual-shore and tiered expertise involving board-certified physicians in dataset structuring to capture diagnostic nuance. This approach, while more resource-intensive, creates the foundation for systems that respect clinical complexity.
Looking Forward
As someone who has straddled the worlds of healthcare and AI development, I believe we’re approaching an inflection point in healthcare’s technological evolution. The transition from passive to agentic AI systems will fundamentally reshape clinical workflows, but only if we maintain a commitment to augmenting rather than replacing human judgment.
These systems should function like the best healthcare professionals—eager to learn, ready to assist, but always aware of their limitations and respectful of expert experience. When implemented thoughtfully, agentic AI promises to return something precious to healthcare providers: the time and mental space to focus on the uniquely human dimensions of healing.
Sina Bari MD is the Associate Vice President of Healthcare and Life Sciences AI at iMerit Technology. His work focuses on the intersection of clinical practice and artificial intelligence, with particular emphasis on creating high-quality training datasets for medical applications.